The intersection of robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) is quickly becoming a driving force in the creation of new industries, cutting-edge technologies and increased productivity and efficiency in existing sectors. As the field of AI in robotics continues to evolve, its applications in the real world are becoming increasingly apparent.
From self-driving cars, customer service and healthcare, to industrial and service robots, AI plays a critical role in transforming industries and daily life. While there are concerns about job displacement due to AI and robotics, the World Economic Forum predicts that technological advancements, including AI, will contribute significantly to global employment, with an estimated 78 million net new jobs created across industries by 2030. This growth highlights the importance of reskilling and education to prepare workers for the evolving demands of a technology-driven future.
Read on to learn more about AI in robotics, plus how you can play a role in the future of this important industry.
What Are Robotics and Artificial Intelligence?
The field of robotics involves designing, building and operating machines capable of performing tasks autonomously or semi-autonomously. These machines, often used to handle repetitive or dangerous tasks, enhance safety, productivity and efficiency in various settings.
Artificial intelligence focuses on creating systems that simulate human intelligence, enabling machines to analyze data, recognize patterns and make decisions. AI powers technologies such as speech recognition, predictive analytics and autonomous navigation.
Together, robotics and AI contribute to intelligent machines capable of adapting to their environment, transforming industries like healthcare, agriculture and logistics.
Are AI and Robotics the Same Thing?
While robotics and AI are closely linked, they are distinct fields with separate objectives and methodologies. Robotics focuses on the physical aspects of machines, designing and building hardware that performs specific tasks, such as a robotic arm assembling products or a drone delivering packages. These systems often rely on pre-programmed instructions to function.
AI, on the other hand, is the “brain” behind intelligent systems. It involves software capable of learning, reasoning and making decisions — abilities that allow machines to respond dynamically to changing conditions. For example, AI enables a chatbot to provide personalized customer support or a car to navigate autonomously.
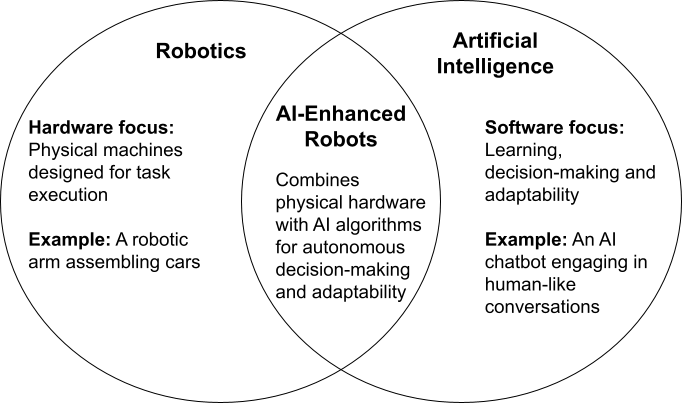
When combined, robotics and AI result in advanced systems that blend physical capabilities with intelligence. AI-powered robots can perceive their surroundings, process data in real time and make informed decisions, making them essential in industries that require precision, adaptability and autonomy.
How AI Is Used in Robotics
Intelligent robots are no longer futuristic concepts but integral assets to various industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to logistics and consumer services. According to recent market reports, the AI robotics market was valued at $15.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to $111.9 billion by 2033, with an annual growth rate of 22.1%. Over 3.5 million industrial robots are operational worldwide, highlighting how automation and intelligent systems are transforming workflows.
Robots equipped with artificial intelligence can analyze data, adapt to new scenarios and perform tasks with precision that surpasses traditional automated systems. AI’s integration into robotics enhances capabilities like natural language understanding, machine learning and computer vision, making robots smarter, more flexible and more autonomous. Here are key ways AI is used in robotics today:
- Machine Learning: AI enables robots to learn from experience and improve over time. For instance, robots can analyze vast datasets to optimize performance in tasks such as assembly line processes or navigation in dynamic environments.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Robots equipped with NLP can interpret and respond to human language. This capability powers applications like customer service robots or humanoid robots that interact with users in retail or healthcare settings.
- Computer Vision: AI allows robots to process visual data for tasks such as object recognition, quality control and navigation. This capability is essential for autonomous vehicles and drones operating in complex environments.
- Edge Computing: AI-powered robots utilize edge computing to process sensor data locally in real-time, enabling fast, agile decision-making. This is particularly valuable in applications requiring quick responses, such as autonomous manufacturing robots.
- Conversational AI: Advanced conversational AI enables humanoid robots and virtual assistants to simulate human-like interactions. This is transforming roles in customer service, training and companionship.
- Collaborative Robotics (Cobots): AI boosts the functionality of cobots, enabling them to safely and effectively work alongside humans in industrial settings. These robots assist with repetitive or physically demanding tasks while adapting to human workflows.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI enables robots to monitor equipment health and predict failures before they occur. This reduces downtime and optimizes operational productivity in industries like manufacturing and logistics.
- Digital Twin Technology: Robots are now trained in virtual environments, known as digital twins, where they simulate real-world scenarios to optimize performance and safety. This approach accelerates training and reduces the risks of deploying robots in physical environments.
As AI technologies continue to advance, their integration with robotics is expected to expand, unlocking new possibilities for innovation and proficiency across industries.
9 Applications of AI in Robotics in Different Industries
The integration of AI in robotics is revolutionizing industries worldwide, enabling smarter systems and more streamlined operations. From agriculture to aerospace, smart robots are solving complex challenges and opening new opportunities for innovation.
Here are nine examples of how AI and robotics are transforming different sectors:
1. Agriculture
AI-powered robots are optimizing farming practices by automating labor-intensive tasks and improving efficiency.
- Precision weeding: Robots like Ecorobotix use AI to identify and spray weeds with pinpoint accuracy, reducing chemical usage and promoting sustainable farming.
- Harvest automation: Robots equipped with computer vision, such as the Burro autonomous platform, assist in harvesting crops like fruits and vegetables, addressing labor shortages in the agriculture sector.
2. Aerospace
The aerospace industry leverages intelligent robotics for precision and safety in environments beyond human reach.
- Space exploration: NASA employs robotic arms with AI to assemble spacecraft and conduct maintenance in space.
- Autonomous inspection: Drones and robotic systems with AI capabilities inspect aircraft and monitor for structural issues, ensuring safety and reducing downtime.
3. Automotive
The automotive industry is at the forefront of adopting AI and robotics for manufacturing and innovation.
- Assembly line automation: Tesla’s AI-powered robots improve performance and precision in electric vehicle production.
- Self-driving technology: Self-driving tech is progressing, with AI enabling navigation, obstacle detection and decision-making. Innovations such as improved vision transformers enhance the vehicle’s ability to map and interpret their surroundings, moving closer to full autonomy.
4. Food Service
AI in robotics is automating food preparation and improving efficiency in the hospitality industry.
- Cooking assistance: Robots like Miso Robotics’ Flippy automate cooking tasks, including flipping burgers and frying chicken, ensuring consistency and reducing labor costs.
- Order fulfillment: AI-enabled robot waiters streamline the food service process by transporting meals directly to customers.
5. Healthcare
Smart robots are bettering patient care, improving precision in surgeries and easing workloads for medical professionals.
- Surgical assistance: Robots like the da Vinci Surgical System utilize AI for enhanced precision during minimally invasive procedures, which could reduce patient recovery times.
- Rehabilitation support: AI-powered robotic exoskeletons assist patients recovering from injuries or surgeries by providing physical support and real-time feedback.
6. Household Products
Robotics integrated with AI is making everyday life more convenient and effective.
- Home cleaning: The Roborock Saros Z70 features an AI-driven folding arm that can detect and remove small obstructions like socks or towels, setting a new standard for intelligent and adaptable household cleaning robots.
7. Manufacturing
AI and robotics are driving advancements in smart factories and Industry 4.0 initiatives.
- Predictive maintenance: Robots equipped with AI perform inspections and repairs in hazardous areas. For example, robots like the Metalspray PipeID Rover apply protective coatings inside pipelines, reducing corrosion and minimizing maintenance-related downtime.
- Quality control: Intelligent vision systems inspect products for defects, improving product reliability and reducing waste.
8. Military
The military uses AI robotics for reconnaissance, logistics and operational efficiency in challenging environments.
- Autonomous vehicles: AI-driven drones and ground robots — some of which have been used recently to combat the Russian invasion of Ukraine — conduct surveillance and assist in supply delivery in dangerous or remote areas.
- Explosive ordnance disposal: Robots with AI capabilities safely handle and neutralize explosive devices, protecting human operators.
9. Postal and Supply Chain
AI robotics is streamlining logistics and delivery processes to meet the growing demands of e-commerce.
- Automated sorting: Robots like Boston Dynamics’ Stretch use AI to sort and move packages within warehouses.
- Last-mile delivery: Autonomous delivery robots transport packages to customers, reducing delivery times and costs.
What Is a Robotics Engineer?
As robotics continue to shape various industries, a robotics engineer plays a critical role in robotic design, maintenance and functionality. A robotics engineer is a specialist responsible for building, installing and maintaining the machines that perform tasks in sectors such as manufacturing, security, aerospace and healthcare.
The day-to-day responsibilities of a robotics engineer include:
- Installing, repairing and testing equipment and components
- Performing predictive maintenance
- Incorporating relevant technical literature into their understanding of system operations
- Identifying new data sources
- Building working relationships
- Ensuring that software solutions meet customer needs
- Developing and deploying AI governance structure to manage ongoing implementation of AI strategies
- Continuously evaluating and reimagining processes to incorporate conversational AI
- Maintaining knowledge of safety standards and regulations for the safe operation of a system
To become a robotics engineer, a bachelor’s or master’s degree in computer engineering, computer science, electrical engineering or a related field is required. Fluency in multiple programming languages and proficiency in algorithm design and debugging are also important qualifications. A successful robotics engineer is also a continuous learner, a natural problem solver and is driven toward ongoing improvement.
The average salary for a robotics engineer is $100,205* per year, making it a lucrative and in-demand career path for those with the right qualifications and skills.
*Salary average according to Glassdoor as of February 2023.
Future of AI in Robotics
The future of AI in robotics is vast and exciting. The next stage of AI, known as AGI or Artificial General Intelligence, holds the potential to reach levels of true human understanding. The key to this is integrating the computational system of AI with a robot. The robot must possess mobility, senses (such as touch, vision and hearing) and the ability to interact with physical objects, which will enable the system to experience immediate sensory feedback from every action it takes. This feedback loop enables the system to learn and comprehend, bringing it closer to achieving true AGI.
The current focus on AI in robotics is shifting from the question of what tasks robots can perform for people, to what type of input a robot can provide the AI’s “mind.” By allowing AI to explore and experiment with real objects, it will be possible for it to approach a deeper understanding, much like a human child. With this integration of AI and robotics, we can expect to see significant advancements in a wide range of industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to security and space exploration.
The future of AI in robotics is bright and holds the potential for tremendous progress in how we understand and interact with the world. By combining the computational power of AI with the physical capabilities of robots, we are opening up new doors for exploration and innovation, and the potential for true AGI is within reach.
Webinar
Ready to Lead the Field of AI and Robotics?
Find out how the University of San Diego’s Master of Science in Applied Artificial Intelligence program can help you develop the skills and knowledge to thrive in this field. Check out the program’s on-demand career webinar to explore industry insights and career opportunities.




