A Career-Building Professional Growth Experience for Lifelong Learner-Educators
What is an MEd degree? The obvious answer is that MEd stands for Master of Education — a graduate-level academic degree that is also sometimes referred to as a master’s in education. However, there are a wide variety of additional ways to answer this seemingly simple question. Read on for a comprehensive look into all things MEd
What Is an MEd Degree?
An MEd degree is a graduate degree that many educators pursue for reasons such as improving teaching practices, making a greater impact on students’ learning and development, and learning how to explore effective approaches for creating inclusive learning environments. Earning an MEd can also increase an educator’s salary range and open doors to more education-related opportunities both in and outside of the classroom. In fact, 88% of large school districts offer additional pay to teachers who hold a master’s degree.
What You Need to Know About a Master of Education Degree
A Master of Education program is designed for practicing teachers and administrators looking to elevate their educational knowledge and practice. It will prepare educators to provide leadership in educational settings and enhance student learning. Depending on the program there may be an additional focus on social justice, school management, leadership, inclusivity excellence or other subjects. A Master of Education program may have specialization tracks like Specialized Learning, Curriculum Instruction, Educational Technology, Inclusive Learning, STEM/STEAM or Administration.
Courses may include:
- Social Justice and Educational Equity
- Cognition and Learning
- Educational Research Methodology
- Qualitative Methods in Educational Research
For those interested in pursuing an MEd or any advanced degree, it’s important to conduct research into potential programs and future career opportunities and salary. An MEd is an investment and it’s important to make an educated choice when committing to it.
We invite you to continue reading and learn more about:
- How an MEd compares to other common education degrees
- Who should consider earning a Master of Education degree
- How an MEd can improve your career
- Teaching jobs you can get with an MEd [plus salary data]
- Non-teaching jobs you can get with an MEd [plus salary data]
- Frequently asked questions
What’s the Difference Between an MEd, a Master of Arts in Teaching and a Master of Science in Teaching?
Each degree program differs by college or university, but many follow a similar curriculum and graduation requirements. Most MEd and MAT programs will require more hands-on experience and less research than an MST, but this is not always the case. One college or university MEd program may have a STEM specialty, while at another college or university, the STEM specialty could fall under an MST.
We’ve gathered some helpful information to help compare the three degree programs. (Sources: USD research and Noodle.com)
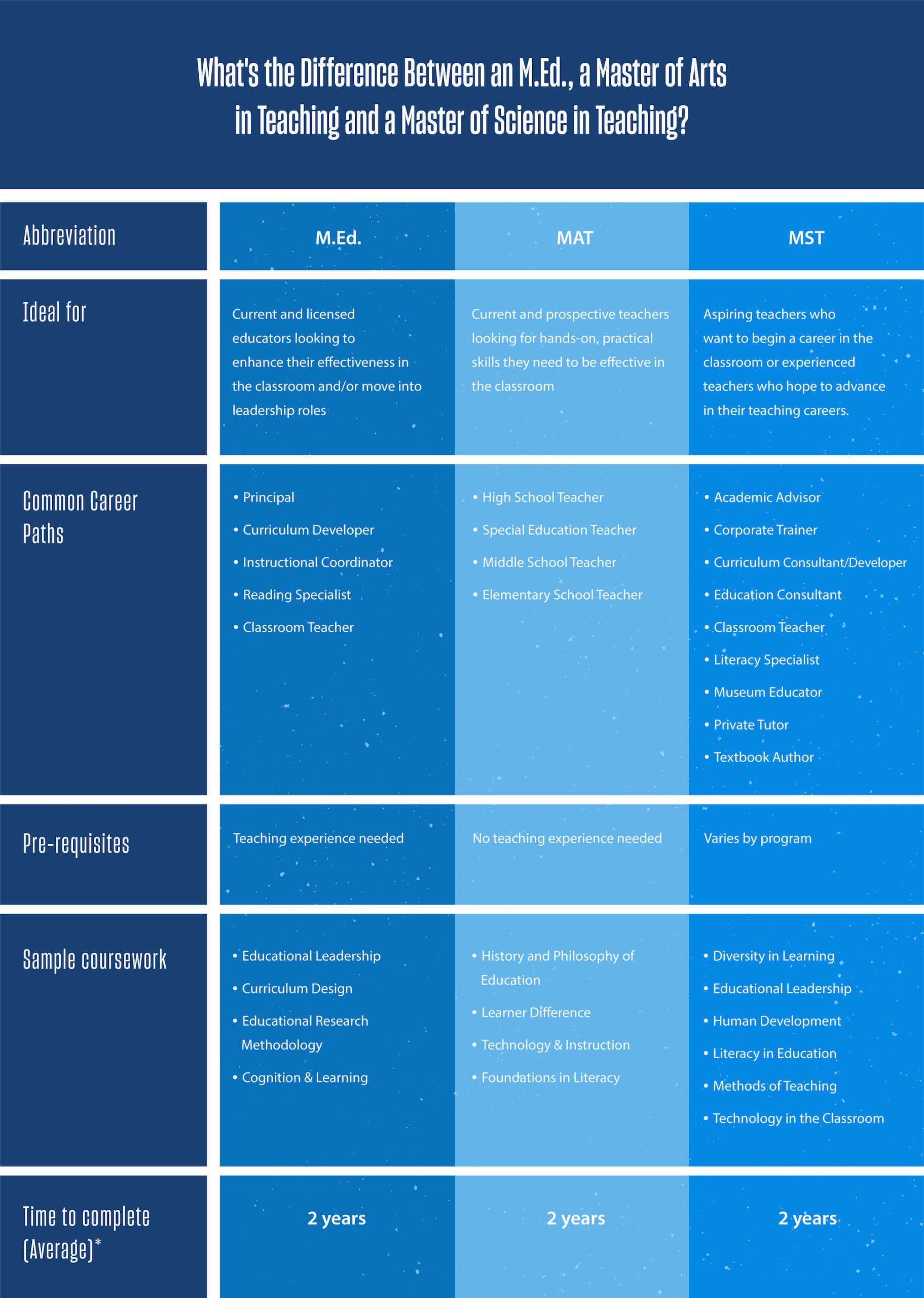
*This will depend on the program and how many credits are taken at once.
Who Should Consider Earning an MEd Degree?
Any educator looking to expand their knowledge of teaching theories and make a greater impact in the lives of students should consider earning an MEd degree. This includes teachers, administrators, counselors, specialists and more. In many of the roles cited above, your Master of Education degree can also position you to earn higher pay — both by being better qualified for higher-level jobs and, in the public school setting, potentially qualifying for district-specific payscale increases.
It’s more accessible now to earn an MEd since many programs are offered nights and weekends or online. Many students pursue their degree while working full-time jobs, raising families and multi-tasking with other responsibilities. There are many students in the USD MEd program, like Chary Salvador, who relied on the flexibility of the program for success.
As she stated, “I like it because it enables me to work at my own pace and I’ve been able to balance my life with the online format. I know the deadlines. I know what’s expected of me.”
[RELATED] 10 Tips for Earning Your MEd While Teaching Full Time >>
How Can a Master of Education Degree Improve My Career?
There are numerous ways that a Master of Education degree can improve your career. Here are just a few:
- Advance your career in teaching
- Become an even more effective teacher
- Reinvigorate your passion for teaching
- Improve your skills and knowledge
- Transition into other school-based roles
- Pursue an education-related opportunity outside the classroom
- Build a foundation for educational leadership opportunities
- Make a greater impact in the education of your students
Many programs, like the USD MEd program, offer specialized tracks in subjects like School Leadership, Technology and Innovation, STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, the Arts and Mathematics), Inclusive Learning, Curriculum and Instruction, and Literacy and Digital Learning.
You may find interest in a specialty like Dr. Curtis Taylor did in the STEAM program. “Because my affinity was toward mathematics, I wanted to go into the STEAM field,” said Taylor, who noted that his studies at USD helped him “understand clearly how to teach mathematics and how students think about mathematics.”
What Teaching Jobs Can I Get with a Master of Education?

As mentioned above, though the MEd is not always the chosen academic option for new teachers, it is a common pathway for working teachers who are interested in improving their skills and knowledge in their current area of specialty or expanding their skills and knowledge to transition into another school-based role. As such, the MEd can be beneficial for educators interested in the following positions:
- Kindergarten Teacher — $60,660
A kindergarten teacher may work in a public or private school. They will guide students in basic subjects and prepare them for elementary school. - Elementary School Teacher — $60,660
Depending on the school, elementary school teachers may teach up to 6th grade. They will teach basic subjects and prepare students for more schooling. - Middle School Teacher — $60,810
A middle school teacher educates students, typically in grades 6 or 7 through 8 or 9, to prepare them for high school. - High School Teacher — $62,870
High school teachers usually specialize in a subject and prepare students with academic lessons and skills to enter the job market or attend college. - Special Education Teacher — $61,500
A special education teacher works with students who may have a range of learning, mental, physical or emotional disabilities. A special education teacher may work in a pre-, elementary, middle or high school. - English Teacher — $60,000+
An English teacher may teach at an elementary, middle or high school. Salary will depend on location, years of experience, certifications, level of education and more. - Art Teacher — $46,385
The responsibilities of an art teacher vary greatly depending on the age of the students, projects or school initiatives as well as location and environment. - Music Teacher — $51,183
A music teacher may teach at any education level. The responsibilities will vary depending on the age and abilities of students, as well as the location and school initiatives. - Educational Technology Specialist — $64,850
An educational technology specialist will be up to date on technology trends and may train students, faculty and administration in software programs. - Technology Resource Teacher — $51,160
A technology resource teacher may assist students with instruction and guide students on how to use technology correctly and respectfully.
What Non-Teaching Jobs Can I Get with a Master of Education?
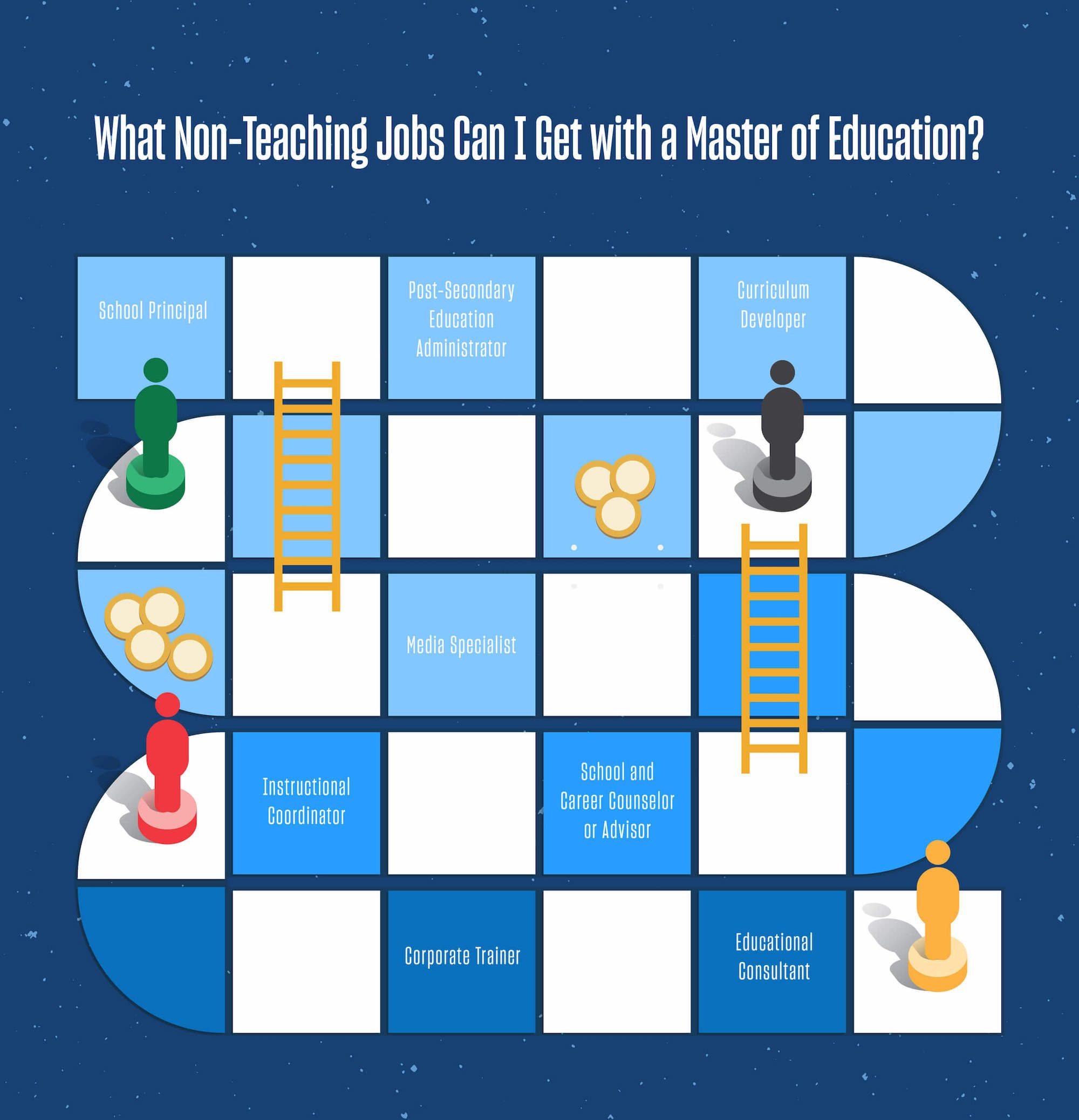
There are a variety of non-teaching jobs that you can get with a Master of Education. Here are just a few highlights:
- School Principal – $98,490
A school principal may work in an elementary, middle or high school and oversees school operations and daily activities. - Post-Secondary Education Administrator – $97,500
A post-secondary education administrator will work at a college or university and oversee academics, student services and faculty research. - Curriculum Developer – $74,900
A curriculum developer will work with subject matter experts to design a learning program and make sure goals of the program are met. - Media Specialist – $56,710
Depending on the specific job responsibilities, a media specialist may curate digital materials and resources for schools, libraries, companies and media outlets. - Instructional Coordinator – $66,970
An instructional coordinator may oversee curriculum and teaching standards for a school, and develop, implement and assess the effectiveness of instructional materials. - School and Career Counselor or Advisor – $58,120
A school and career counselor or advisor may work in a college, university or high school. They will assist students with academic and employment-related tasks. - Corporate Trainer – $57,602
A corporate trainer may be hired internally or externally to implement an employee training program for a business. - Educational Consultant – $103,701
An education consultant may develop teaching programs and curriculum. They may work with any grade level or experience.
Additional non-teaching roles may include:
- Educational Coordinator/Director at Museum, Aquarium, Zoo, etc.
- Private tutor
- Standardized test developer
- Test prep specialist
- Textbook author
[RELATED] Teachers: Is There a Master’s Degree in Your Future? >>
DISCLAIMER: Salary estimates vary and are often adjusted in real time based on changing data. Salary figures listed here are estimates from leading employment sites such as the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, LinkedIn, Springboard, Glassdoor, ZipRecruiter, Indeed and Salary.com.
MEd Degree FAQs
Master of Education (MEd) Articles and Resources
Association of American Educators (AAE)
The AAE is the largest non-union, national professional educator’s organization dedicated to educational advocacy, professionalism and teacher representation.
National Education Association (NEA)
The NEA, the largest labor union in the US, is comprised of over 3 million people interested in the power of public education and inclusivity.
Western Association of Schools and Colleges (WASC)
The WASC is an accreditation regulator of elementary, secondary, nonprofit and supplementary educational programs.
University of San Diego Master of Education Webinar & Information Resource Center
The University of San Diego has recently launched an MEd resource center featuring a growing library of helpful webinars, videos, blog posts and subject matter guides. Here are just a few highlights.
Webinars
- Teaching Race in the Classroom: Philosophy, Strategies and Techniques
- Top Online Teaching Myths & Best Practices for Educators
Blog Posts
- Online Learning More Important Than Ever in the Face of COVID-19 Crisis
- Remote Teaching Resources [Navigating the COVID-19 Crisis]
- Teacher Salaries Have Increased Significantly Over Time — Or Have They?
Subject Matter Guides
- The Complete List of Teaching Methods
- Edutainment in the Classroom: How Technology Is Changing the Game
Downloadable Guides
- Top 9 Reasons to Get Your Master of Education Degree
- 10 Traits of Successful School Leaders
- A Career Advancement Guide for Educators
Only you can decide if an MEd degree is right for you. If you’re interested in pursuing a degree, we’d love to hear from you. Our highly regarded online Master of Education degree program is passionately committed to our mission of providing affordable, high-quality advanced degree opportunities for educators, while also serving as an advocate and thought leader for the education community.




